Cables Blog
Booted vs. Bootless Ethernet Cables: Which Should You Buy?
Choosing Between Booted and Bootless Ethernet Cables
Which cable you should purchase depends on what environment you mean to install your cable in.
by Vikas Dayal • December 10, 2024
Cat5e / Cat6 Cables, ethernet cables
Some network patch cables feature molded plastic boots meant to relieve stress on the cable as well as ensure that it remains in place, while cables without boots are better for use in crowded network switches. Which cable you should purchase depends on what environment you mean to install your cable in.
When setting up a reliable wired network, the type of ethernet cable you choose can make a difference—not just in performance but also in installation and maintenance. Among the many cable options, booted and bootless Ethernet cables are two popular types, each suited to different scenarios. Understanding their features, benefits, and ideal use cases will help you make an informed decision for your specific networking needs. In this guide, we’ll dive into the differences between these cables and outline when to use each one.
What Are Booted Ethernet Cables?
Booted Ethernet cables feature a protective rubber or plastic sleeve, called a boot, at the point where the cable meets the connector. This boot provides added durability and reduces the risk of wear and tear over time. There are two main types of boots:
- Snagless Boots: These have a tab cover that prevents the clip from getting caught on other cables or objects during installation.
- Molded Boots: These offer a more seamless look and additional protection to the connector’s clip.
Booted cables are commonly used in environments where cables might be frequently moved, unplugged, or bent. The extra protection ensures that the connectors remain intact, even in demanding conditions.
Consider, for example, our Cat6A 24AWG Yellow Snagless Ethernet Network Patch Cable. This particular cable has a lot going for it - it's shielded for protection in environments with a lot of EMI interference and is fast enough for gigabit applications, featuring RJ45 plugs that are 50 micron gold plated. These traits make it ideal for use in Office VOIP, data, and home networks. And like many of Cables.com's Datacomm cables, it's covered under a lifetime warranty.
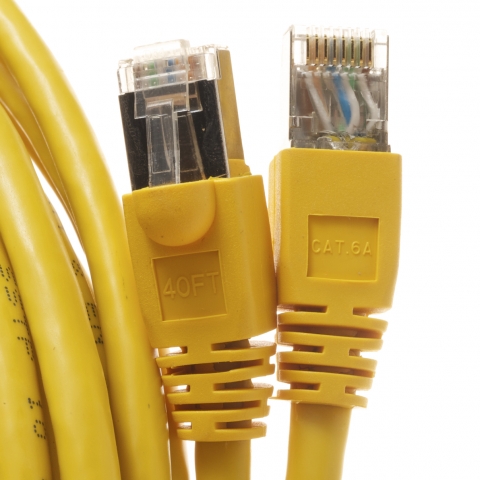

Cables.com stocks a variety of cables with the snagless boot feature, including our Cat6 network patch cables rated for up to 550 Mhz. But what about our bootless ethernet cables? When would a patch network cable with no boot be the better option for you?
What Are Bootless Ethernet Cables?
Bootless Ethernet cables, as the name suggests, lack the protective boot around the connector. They have an exposed clip that makes it easier to plug and unplug the cable. This streamlined design is especially beneficial in applications where space is tight or where cables are rarely moved after installation.
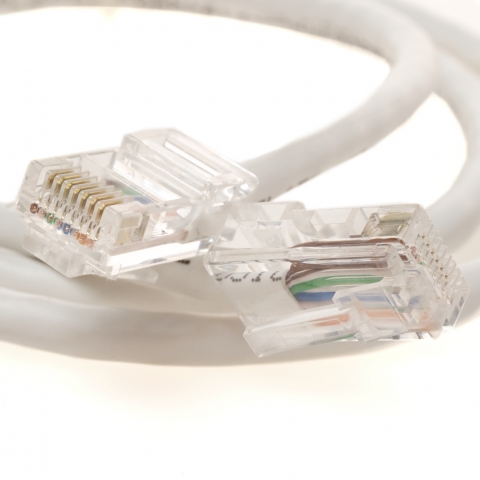

This is our Cat6 550Mhz Network Cable. As you can see, this cable doesn't have the molded plastic hood that links the RJ45 connector to the body of the cable like the booted cable did. You might think that can put your connection at risk - why wouldn't you want a boot? The answer is that not all cables are going to be installed in the same environment. A booted cable might be a good fit beneath a desk, but in a high density network switch environment where there might be many cables running alongside it, the added bulk of the boot takes up precious space. If you don't expect your network patch cable to be handled much, a bootless cable will do you just fine! And you'll get the same stellar performance you'd get from a cable with an attached boot.
Because they lack the added material of a boot, bootless cables are often slightly more compact and lightweight. This makes them a popular choice for environments where cable management and space optimization are key considerations.
Key Differences Between Booted and Bootless Cables
- Durability:
- Booted cables offer better protection against physical damage and wear.
- Bootless cables are more susceptible to damage, especially in high-traffic or high-stress environments.
- Ease of Use:
- Booted cables can be harder to plug and unplug, particularly in tight spaces.
- Bootless cables are easier to handle and connect in confined areas.
- Cable Management:
- Booted cables’ added bulk can make them harder to manage in dense cable bundles.
- Bootless cables’ slimmer design makes them ideal for organized setups.
- Aesthetics:
- Booted cables often look more polished and professional.
- Bootless cables have a minimalistic and straightforward appearance.
When to Use Booted Ethernet Cables
Booted cables are best suited for:
- High-Traffic Areas: In environments like offices or data centers where cables are frequently accessed or moved, booted cables provide the durability needed to withstand constant handling.
- Outdoor or Industrial Settings: The additional protection can safeguard against environmental factors like dust, moisture, or physical strain.
- Temporary Installations: If cables will be plugged and unplugged repeatedly, the boots help extend the lifespan of the connectors.
When to Use Bootless Ethernet Cables
Bootless cables are ideal for:
- Tight Spaces: In crowded racks or behind furniture, their slim profile makes installation and adjustments easier.
- Permanent Installations: For cables that will remain stationary for long periods, the lack of a boot is less of a concern.
- Cost-Conscious Projects: Bootless cables are often slightly more affordable, making them a good option for large-scale installations with fixed budgets.
Making the Right Choice
When deciding between booted and bootless Ethernet cables, consider the environment, frequency of use, and specific requirements of your network. If durability and protection are priorities, booted cables are the clear winner. However, if ease of installation and space-saving are more critical, bootless cables may be the better choice.
Both options have their place in modern networking. By evaluating your needs and understanding the strengths of each type, you can ensure that your network setup is both functional and efficient.